Lithium aluminium hydride LiAlH 4 is one of the few reagents that can reduce an acid to an alcohol. Caprylyl Glucoside Octyl Glucoside.

Alkane Degradative Pathways A Terminal Oxidation Of N Alkanes A And Download Scientific Diagram
How Can We Convert Alkane To Alcohol Quora
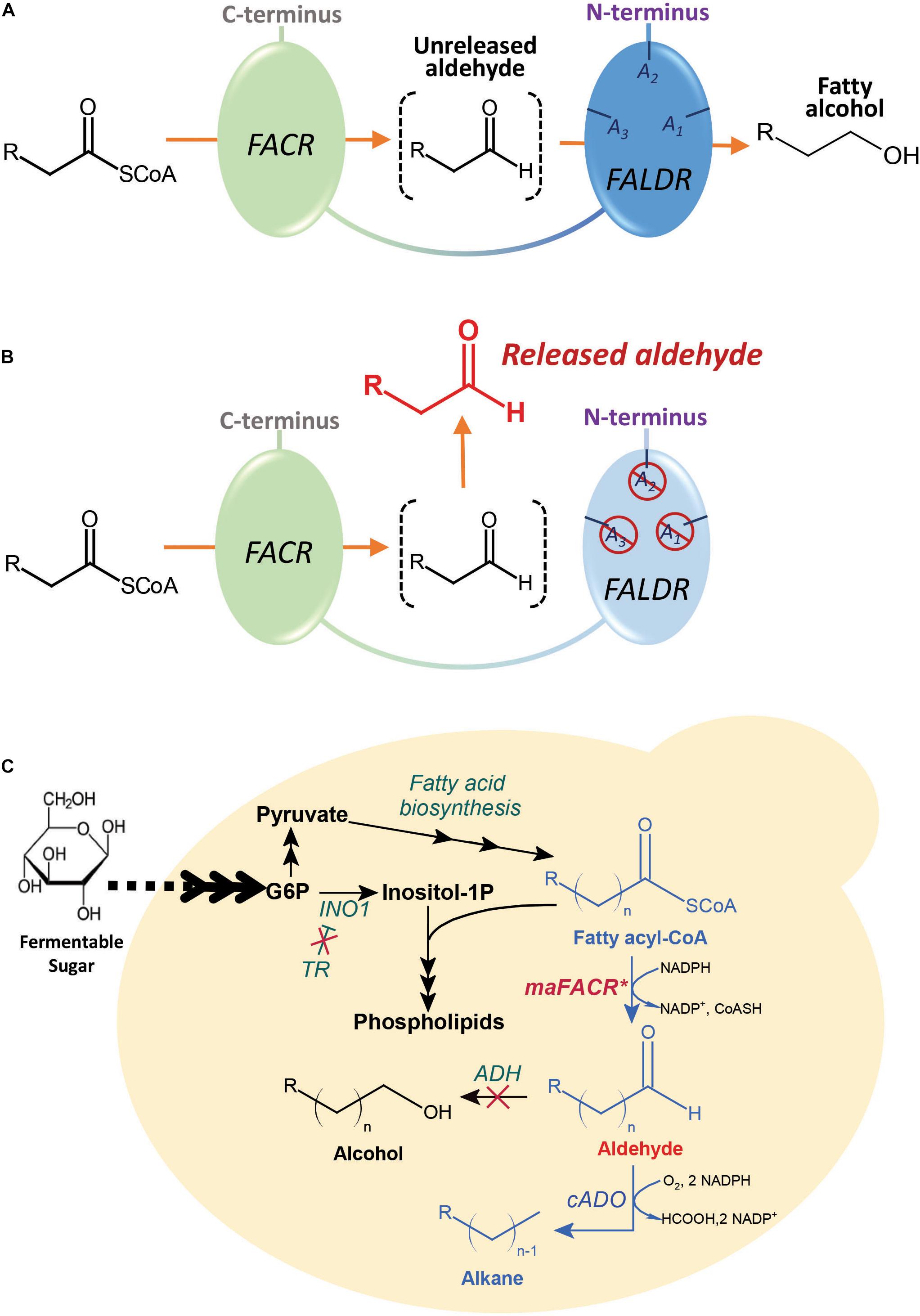
Frontiers Engineering An Alcohol Forming Fatty Acyl Coa Reductase For Aldehyde And Hydrocarbon Biosynthesis In Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Bioengineering And Biotechnology
270 F 1322222 C NIOSH EL5425000 130 C Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations 3-Methyl-1-butanol.

Alkane to alcohol. Biodegradable surfactant cleaning agent Glycereth cocoate. Alcohol - alcohol - Structure and classification of alcohols. 130 C SynQuest 73779.
Alkenes - lineare saturated molecules straight or branched chains Olefins. Non-ionic surfactants cleaning agents. 130-132 C Alfa Aesar L13660 36716.
It has been found in Jeffrey pine Pinus jeffreyi. Alcohols are hydrocarbon compounds with one or two hydroxyl groups replacing one or more hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon. An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is connected to an alkane.
Alcohols have the general molecular formula C n H 2 n1 OH. Condensation of the carbonyl compound with hydrazine forms the hydrazone and treatment with base induces the reduction of the carbon coupled with oxidation of the hydrazine to. Isopropanol Isopropyl alcohol 67-63-0.
It has a role as a non-polar solvent and a plant metabolite. An organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group OH is bound to a saturated carbon atom. If the halogen is bonded to a simple alkyl group an alternative alkyl.
Some prominent physical and chemical properties of alcohols are given below. According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry IUPAC alcohols are named by changing the ending of the parent alkane name to -olHere are some basic IUPAC rules for naming alcohols. In oil industry the following terms for the different hydrocarbons are used.
4RCOOH 3LiAlH 4 4RCH 2 OH 1 o alcohol. 132 C OU Chemical Safety Data No longer updated More details. The membrane is held together because the alkane chain of a fatty acid is hydrophobic.
Alkanes have the general chemical formula C n H 2n2The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of. The molecular electrostatic potential is the potential. Structure properties spectra suppliers and links for.
According to IUPAC system Unit 12 Class XI the name of an alcohol is derived from the name of the alkane from which the alcohol is derived by substituting e of alkane with the suffix ol. Physical Properties of Alcohol 1. Grignard reagent behaves as a nucleophile and get the hydrogen atom from the alcohol group.
This is due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups of alcohol molecules. Because of the excellent yields it gives LiAlH 4 is a common ingredient in the laboratory for the reduction of not. Conversely an alkane would be expected to show the opposite solubility behavior.
Fluoro F- chloro Cl- bromo Br- and iodo I-. B 2-methylpentane C 3-methylpentane D 22-dimethylbutane E 23-dimethylbutane Halogen substituents are easily accommodated using the names. Alkenes - lineare unsaturated molecules straight or branched chains these are normally not present in unprocessed crude oil Naphthenes.
Few carbons and an alcohol functional group FG would be expected to be soluble in solvents that have a few carbons and an alcohol FG or in some other polar solvent and to be less soluble in nonpolar solvents. Hydrolysis saponification of a fat would yield _____. In chemistry alcohol is an organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group OH bound to a saturated carbon atom.
The structures properties and chemical reactions of organic and biochemicals are determined by the functional groups present. They are compared with the equivalent alkane methane to butane with the same number of carbon atoms. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol ethyl alcohol which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinksAn important class of alcohols of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members includes.
Plant derived and food grade biodegradable water softener. In organic chemistry an alkane or paraffin a historical trivial name that also has other meanings is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbonIn other words an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carboncarbon bonds are single. The Boiling Point of Alcohols.
The reduction of aldehydes and ketones to alkanes. In most cases though it is not as simple as this. The position of substituents are indicated by numerals.
To determine if inhaled nephrotoxic branched and nonnephrotoxic straight chain alkanes differ substantially in their biological fate male F344 rats were exposed to 14C-labeled isooctane and octane vapors at approximately 1 and 350 ppm by the nose-only mode for 2 hr. When one puts a protein in ethanol ethyl alcohol the protein can not function properly and becomes denatured. 269-271 F 760 mmHg 1316667.
A an acid and an alcohol b a ketone and an alcohol c an alkane and a ketone d only an acid e an amine and an acid 25. According to the IUPAC nomenclature system an alcohol is named by dropping the terminal -e of the parent carbon chain alkane alkene or alkyne in most cases and the addition of -ol as the ending. If the location of the hydroxyl group must be specified.
For example CH 3 2 CHCH 2 CH 2 Br would be named 1-bromo-3-methylbutane. Amide Acid Alcohol Amine Ether Alkane Organic Functional Group Polarity and Electrostatic Potential. Alcohols generally have higher boiling points in comparison to other hydrocarbons having equal molecular masses.
Alkyl group of Grignard reagents are strong alkalis and nucleophiles. It is a volatile organic compound and an alkane. Alcohol is a homologous sequence of compounds that contain the hydroxyl group as a functional group -OH.
For this the longest carbon chain parent chain is numbered starting at the end. Functional groups are defined as specific groupings of atoms or bonds which are part of a larger hydrocarbon chain. Sulfonic acids C14-16-alkane hydroxy and C14-16-alkene sodium salts.
See chemical bonding for a discussion of hybrid orbitals Alkyl groups are generally bulkier than hydrogen atoms however so the ROH bond angle in. 130 C Literature LabNetwork old LN00163016 132 C FooDB FDB008131. The boiling point of an alcohol is always much higher than that of the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms.
Grignard reagent and alcohol reaction give a hydrocarbon as a product which is an alkane compound in most occasions. Alcohols with one to four carbon atoms are frequently called by common names in which the name of the alkyl group is followed by the word alcohol. For the above isomers of hexane the IUPAC names are.
An organic compound that contains a carboxyl group COOH. Also bacteria are surrounded by a lipid membrane fatty acids. Nomenclature of Alcohols.
Cycloalkanes - saturated ring structures or cycloalkenes - partly saturated ring. Similar to water an alcohol can be pictured as having an sp3 hybridized tetrahedral oxygen atom with nonbonding pairs of electrons occupying two of the four sp3 hybrid orbitals. 130 C SynQuest 73779 2101-1-53.
A water and an alkene b ethanol and propanoic acid c glycerol and soap d ethanol and a soap e a. The boiling points of the alcohols increase as the number of carbon atoms increases. Radioactivity in exhalant urine and feces was determined for 70 hr post exposure after which residual radioactivity in the.
N-heptane is a clear colorless liquids with a petroleum-like odor. Heptane is a straight-chain alkane with seven carbon atoms.

A Novel Reduction Reaction For The Conversion Of Aldehydes Ketones And Primary Secondary And Tertiary Alcohols Into Their Corresponding Alkanes Sciencedirect

Gc Analysis Of Active Amyl Alcohol Isoamyl Alcohol And C10 C14 N Alkane Markers On Slb Il76i

How To Convert Alcohol Alkane To Alkane Chemistry Haloalkanes And Haloarenes 14074647 Meritnation Com

Reaction Pathways Proposed By Seewald 2001a 2003 Among Alkanes Download Scientific Diagram
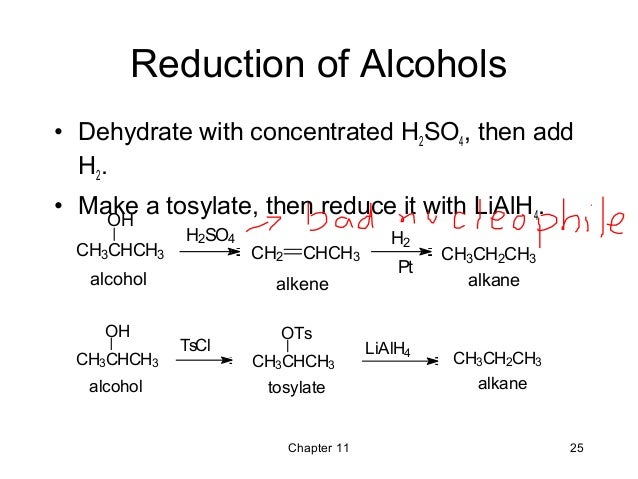
11 Reactions Of Alcohols Wade 7th

Alcohol Reactions Of Alcohols Britannica

Doubt Why Hi Does Not Give Alkane With Trihydric Alcohol Chapter Alcohols Phenols And Ethers Subject Organic Chemistry Course Neet Chemistry Video Module Organic Chemistry
How Can We Convert Alkane To Alcohol Quora
